ANFF-VIC Technology Ambassadors – Class of 2019

ANFF-VIC has welcomed three new Technology Ambassadors in March – Dr David Garrett, Dr Ranjith Unnithan and Professor Peter Kingshott.
Since the TA scheme was initiated in 2011, Ambassadors have been selected from a broad range of disciplines, each with their own unique demands for micro/nanotechnology.
In addition to their core research activities, ANFF-VIC TAs use their considerable expertise to create new processes that benefit the ANFF-VIC user community and undergo in-kind cooperative activities reflecting the current and emerging needs of researchers in their respective fields.
There is now a total 12 ANFF-VIC Technology Ambassadors: Saulius Juodkazis (Swinburne), Qialiang Bao (Monash), Victor Cadarso (Monash), Ranjith Unnithan (UniMelb), Sharath Sriram (RMIT), Grant van Riessen (La Trobe), David Garrett (UniMelb), Anthony Chesman (CSIRO), Peter Kingshott (Swinburne), Udo Bach (Monash), Wenlong Cheng (Monash), Lingxue Kong (Deakin)
Dr David J. Garrett
Senior Research Fellow – University of Melbourne
Dr David Garrett’s career has been aimed at overcoming the limitations of neural interface technology using carbon materials, resulting in a series of patents and more than 40 papers within eight years.
In 2015, Dr Garrett founded a start-up in Canada, based around commercialising a retinal prosthesis developed in his early career.
Dr Garrett will be focused on how to translate devices that harness the properties of nanometre-thick layers of diamond to industrially relevant applications, investigating both the abilities of these devices, and the way they connect with the outside world.
As such the team will be heavily using MCN’s diamond deposition suite, featuring two Seki MPCVD systems that are used for growing ultra-high purity and nitrogen vacancy diamond, or for growing boron-doped diamond.
Dr Ranjith Unnithan
Senior Lecturer – University of Melbourne
Dr Ranjith Unnithan’s research areas span CMOS image sensors, electronic sensors for biomedical applications, thermal image cameras and nanophotonic engineering.
In addition to publishing a string of high-impact papers, Dr Unnithan has demonstrated a talent for commercialising technologies, having won four innovation awards and co-founding Hort-Eye Pty Ltd – a precision drone sensing company – with a team from the University of Melbourne.
Dr Unnithan will be working to improve the ways in which nanostructures are incorporated with electrical devices such as CMOS image sensors. He aims to improve the fabrication process of these nanostructures to allow them to be created directly onto a sensor, which would reduce the size, weight and power consumption of these devices compared to traditional technologies.
Nanostructures are of interest to imaging applications as they can be used to tune a sensor to particular bands of the light spectrum, making them incredibly useful when trying to collect as much information about a field-of-view as possible. However, current methods to create the structures involve the use of heat, vacuums or plasmas which can reduce the sensitivity of the sensor instead of enhancing it – fabrication issues Dr Unnithan hopes to overcome using novel manufacturing processes.
Dr Unnithan’s project will be reliant on MCN’s high-resolution lithography systems, including the NanoFrazor which uses a heated cantilever tip to create structures with a resolution of ~10nm.
Professor Peter Kingshott
Department Research Director – Swinburne University of Technology
Professor Peter Kingshott has built an international profile in the multidisciplinary field of biointerface science – his expertise extends into nanomaterials, colloid and surface science, biomaterials, biomedical engineering, and regenerative medicine.
He has published more than 150 publications, holds a range of patents, and has been the editor for Applied Surface Science for more than five years.
Professor Kingshott and his researchers will be investigating advanced surface nanostructures for biomedical applications with a particular focus on the ways surface topography can encourage or manipulate stem cell growth.
This broad-scoped project will also delve into surface chemistries and patterns that could inhibit the growth or movement of bacteria.
Professor Kingshott will be using a range of both masked and maskless lithography techniques – in addition to characterisation, plasma polymerisation, and atomic layer deposition capabilities – from across the hubs of ANFF-VIC as he conducts his research.
MCN User Satisfaction Survey 2018

We would like to thank all of those that took part in this year’s survey – we have received the largest response to date.
Survey prize winner
Lars Esser has been selected as the winner of the MCN User Satisfaction prize draw, taking home the prize of $200 user credit to be added to his account for future projects.
Lars is a research fellow at CSIRO developing new strategies to diagnose and treat brain cancer.
The results
Overall, 90% of respondents described their experiences with MCN as good or very good, according to five questions relating to access times, quality of service, and communication – a particular highlight was that more than 95% of respondents stated that the consulting expertise of MCN Process Engineers was good, or very good.
The ANFF-VIC management team is now working to build on the successes that were highlighted and identifying the best ways to address the concerns raised within the responses to the survey. The results report will be published shortly after.
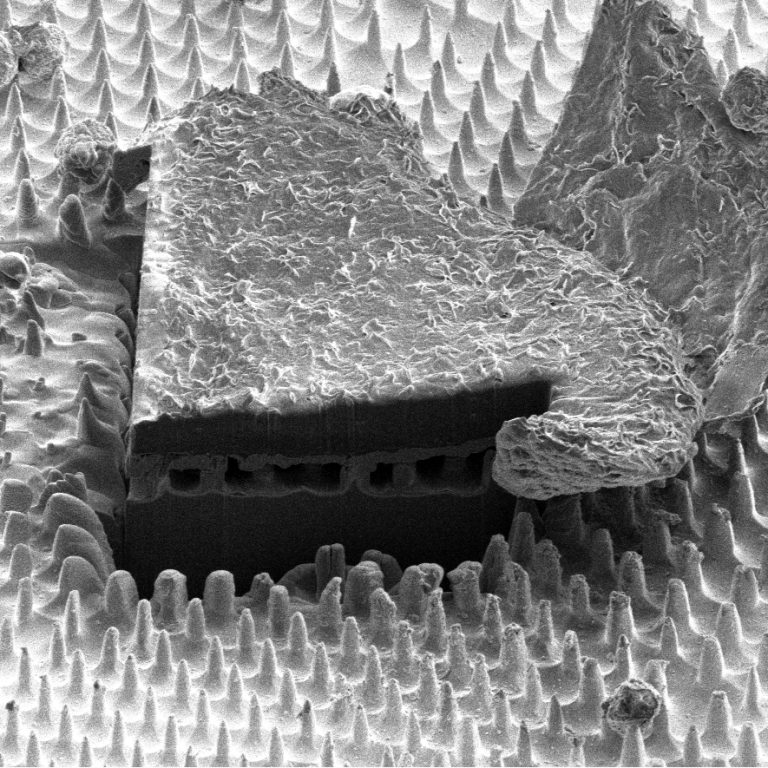
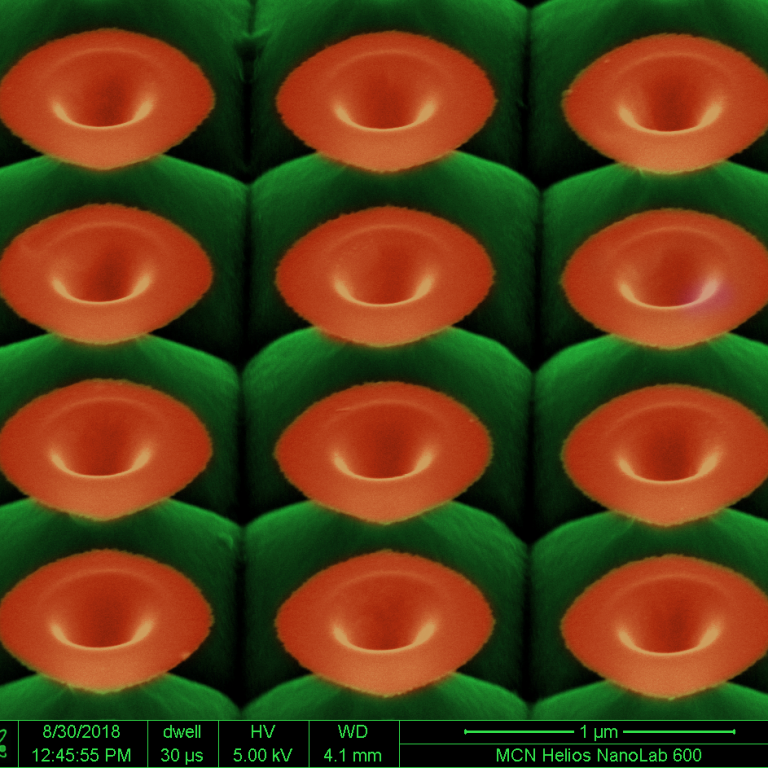
Microscopic Gardening wins Image of the Year 2018
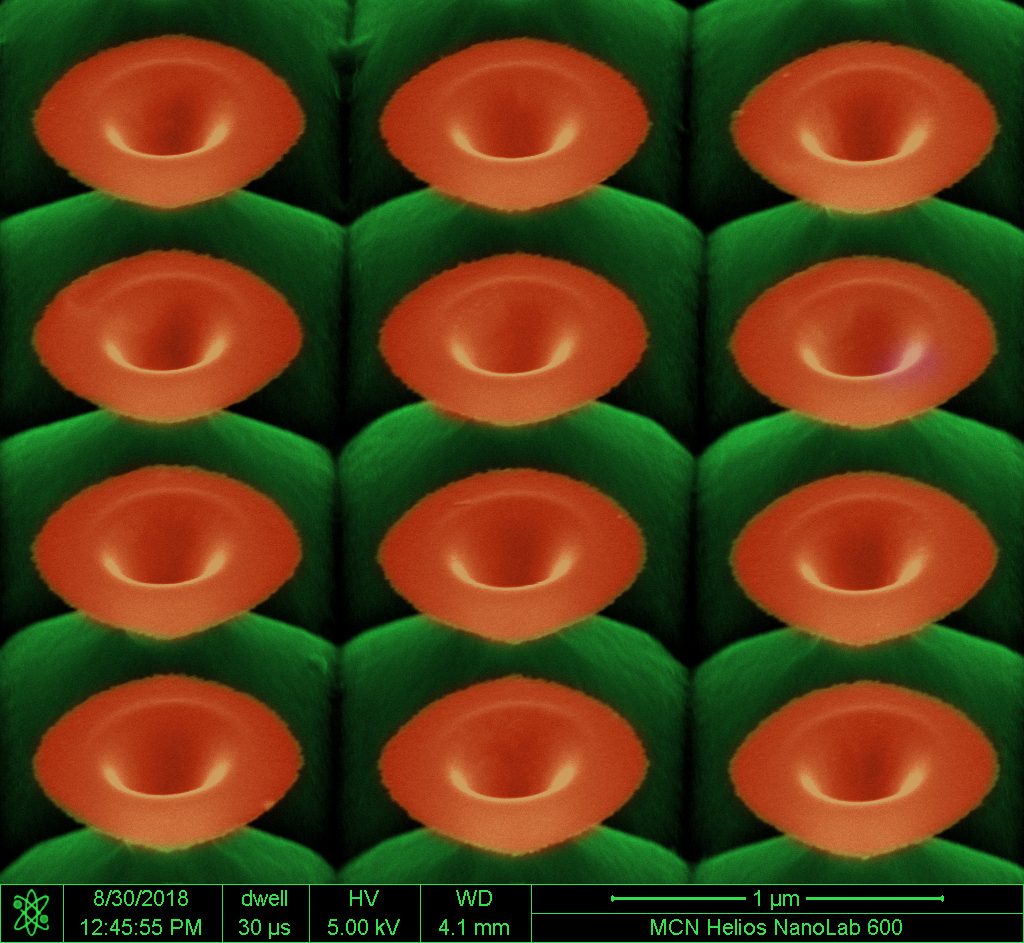
It appears that the ANFF-VIC community has green fingers this year – Microscopic Gardening: Tiny Blossoms of Silicon by Vivek Garg has been voted the ANFF-VIC Image of the Year 2018.
The image shows a scanning electron micrograph (false-color) of Silicon (Si) nanoflowers, created using MCN’s Focused Ion Beam (FIB) in conjunction with wet chemical etching.
As winner of the competition, Vivek will take home a $200 prize.
Vivek and his colleagues are investigating fabrication of 3D freeform structures of Si, such as these nanoflowers, due to their unique optical properties. Such structures can be engineered to selectively absorb light, and produce various colours depending on their architecture – they have tremendous potential for future optics applications such as optical security, polarimetry, and spectral imaging.
“The bulk structuration of Si substrate, based on the ion implantation design and area, allows fabrication of exotic functional and 3D micro/nanostructures on Si substrate exhibiting unique optical properties for applications in nanophotonics and physical sciences,” Vivek explained.
Vivek is a PhD candidate with the IITB-Monash Research Academy, a collaboration between IIT Bombay, India and Monash University, Australia. He is working with Dr Rakesh Mote (IIT Bombay) and Dr Jing Fu (Monash) on the fabrication and controlled manipulation of freeform 3D micro/nanostructures with ion beams. This work is a part of his thesis project, in which he is investigating the use of FIB nanofabrication in creating novel nanostructures for diverse applications such as anti-reflection, colour filtering, sensors and more.
Read more about Vivek’s work here http://www.vivekgarg.org/, or view the full shortlist for the 2018 Image of the Year competition below.