Drug Delivery
Current
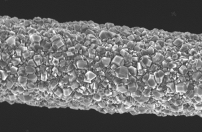
Diamond coating Carbon Fibre
A team of Victorian scientists have coated carbon fibre with diamond, enhancing the material’s usability in medical and sensor applications where the composite material offers huge potential advantages.
Read more...Exploring gold nanowires and nanorods
Professor Wenlong Cheng from Monash University has been exploring unique properties of gold nanomaterials for over 16 years. Two recent projects, conducted at ANFF-Vic’s Melbourne Centre for Nanofabrication (MCN), involved gold nanorods and gold nanowires.
Read more...Fighting resistance to antibiotics
As resistance to antibiotics is becoming increasingly common, it has become even more important to understand the mechanism by which they work on bacterial cells and to develop new antibiotics which can be used agaisnt ’super bugs.’
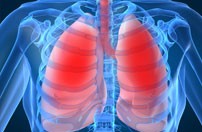
Read more...Cancer treatment to be delivered to lungs
In treating diseases such as lung cancer, tuberculosis, cystic fybrosis and asthma, a large range of intravenous drugs are directed at the lungs but inefficiently delivered. A device is under investigation for the generation and delivery of aerosolised drugs directly to the lungs.
Read more...Archive
A pain-free solution to vaccines
Vaccinations, though vital in preventing the spread of disease in the modern world, have several major drawbacks which limit their effectiveness and uptake in developing countries. Professor Mark Kendall has spent the last ten years developing a needle free solution to immunisation.
Read more...Nano-engineered intelligent delivery systems
Multidrug resistance is a growing problem as methods of treatment that have been relied upon in the past are no longer effective. Together with MCN, researchers from Monash University are looking to develop an intelligent drug delivery system that combats multidrug resistance.
Read more...Safer surgeries with microbots
Microrobots are making minimally invasive, vascular surgery even less invasive and risky. Researchers at MCN have developed a 240 micron diameter micromotor capable of navigating through arteries deep inside the human body.
Read more...Automated systems for cell transfection
Incorporating nanosystems into experiments can provide useful insight into the interaction of nanomaterials within the biological environment, gene expression, targeted cell delivery and encapsulation.
Read more...Liquitab, not a hard pill to swallow
The days of costly liquid antibiotics will soon be over for people who have difficulty swallowing pills. Liquitab has engaged with MCN to develop a unique technology, capable of grinding pills into a palatable liquid.
Read more...Nanoscale study of biological cells
Focused Ion Beam Scanning Electron Microscopes are enabling the study of biological cells on a nanoscale as researchers at MCN and Monash University are utilising the FIB-SEM as well as protein nanoprobes to study protein assemblies and their place within cells.
Read more...Improving cancer therapies
The ability to efficiently deliver large therapeutic molecules into cancer cells, without harming healthy cells remains a largely unsolved technological challenge. Researchers from Monash University are addressing this by developing nanoscale therapeutic carriers, with improved efficacy and specificity.
Read more...